

The final right column contains the assembly version of the machine language instructions, as hex is till not really human readable. 01001110110111, objdump will display the binary as hex, to make it a more human readable format. The second column contains the machine language instructions, that the 圆4 processor reads as binary values. The CPU will access the memory address to retrieve the machine language instructions that make up the compiled program. These bytes of memory can be accessed by going to its memory address. Memory can be seen as a row of bytes that all have their own memory address. The hex numbers on the left, starting with 0x4004f4 are the memory addresses. For this example, 20 lines will be plenty as you can see the end NOPs that are non operation instructions. To dump a sensible amount of lines, you can grep the output to limit the amount of data onscreen.
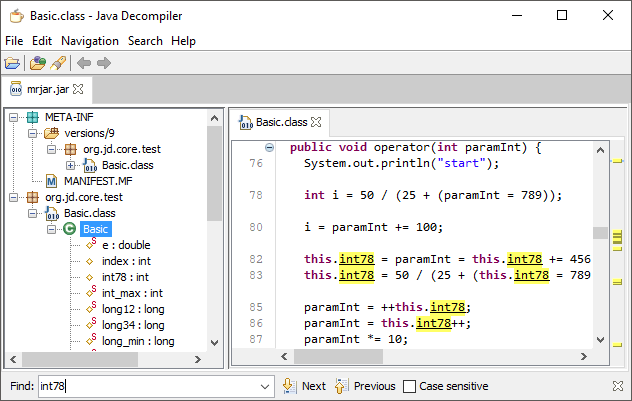
Using objdump you can analyse the binary and how it is interacting with the CPU, in this case within a 圆4 architecture: minh-mint prog # objdump -M intel -D a.out | grep -A20 main.:Ĥ004fc: c7 45 fc 00 00 00 00 mov DWORD PTR ,0x0Ĥ0050f: 83 45 fc 01 add DWORD PTR ,0x1Ĥ00513: 83 7d fc 09 cmp DWORD PTR ,0x9 Depending on your choice of Linux distro, it may come pre-installed or you may need to manually install it. Objdump is contained in the binutils package in your distro. However, if you only have the compiled binary, what could we do to find out what the program is actually doing? With the use of a tool called objdump Generally, if you have the source code, performing reverse engineering to find out what the program does, can be done by trivially reading through the code. Hello, world! Hello, world! Hello, world! Hello, world! Hello, world! Hello, world! Hello, world! Hello, world! Hello, world! Hello, world! Such as gcc: minh-mint prog # gcc hello.c The next step is to compile the code using a compiler, The program simply prints out “Hello, World to the screen 10 times. Comments are shown by the use of // which are ignored by the compiler. This C program will begin with the execution of code at the function main(). Minh -mint prog # cat hello.c int main ( )


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
